Blog / Comparison
Write to UsProxy vs VPN: What's the Difference & Which One Should You Use?
October 22, 2025
Comparison

Proxy vs VPN: What's the Difference & Which One Should You Use?
Online privacy and data control have become essential in today's connected world. Whether you're managing social accounts, scraping data, or running automated tools, hiding your IP address and protecting your activities are key to staying efficient and secure.
Two popular tools for this are proxies and VPNs (Virtual Private Networks). They may appear similar, but they serve very different purposes—and for many modern online tasks, proxies outperform VPNs in speed, flexibility, and scalability.
Here's what sets them apart and why proxies are often the smarter choice.
What Is a VPN?
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) routes your entire internet connection through an encrypted tunnel to a secure server. VPN services create a secure tunnel between your device and a VPN server, encrypting all your internet traffic. This hides your IP address and encrypts your data, making it unreadable to ISPs, hackers, or network administrators.
VPNs are mainly designed for personal privacy and security, especially when using public Wi-Fi or accessing geo-restricted content. A VPN encrypts your data, including sensitive information like login credentials, to protect it from your internet service provider and hackers.
However, because VPNs encrypt all traffic, they tend to slow down your internet speed and are not suitable for large-scale or high-frequency operations such as data scraping or automation. This data encryption enhances network security and ensures that most VPN providers cannot log or monitor your online activity.
For optimal privacy and security, choose a reputable VPN provider or VPN service that offers strong data encryption, a no-log policy, and comprehensive network security features.
What Is a Proxy Server?
A proxy acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet. Instead of sending internet requests directly to a website, your traffic goes through the proxy server, which handles these requests on your behalf and forwards them using its own IP addresses.
This hides your real IP and lets you appear as if you're connecting from a different region or device. A forward proxy is the most common type, acting as an intermediary for internet requests from internal networks.
Unlike VPNs, proxies can be configured for specific applications, browsers, or tools, giving you more granular control and faster performance.
Depending on your needs, you can choose either a proxy server or a VPN—see the next section for a proxy vs VPN comparison.
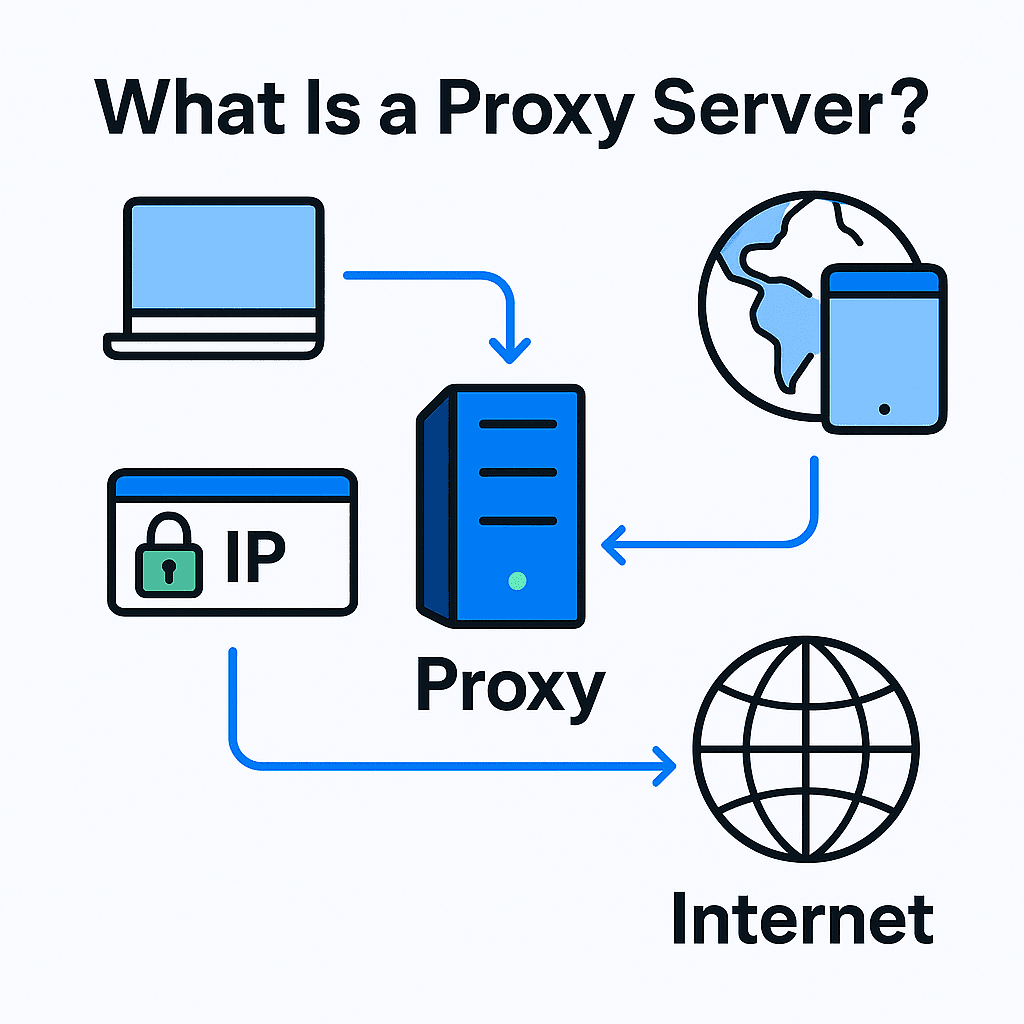
How Proxy Servers Work
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between your device and the wider internet, managing the flow of internet traffic and web requests. When you attempt to access a website, your request is first sent to the proxy server. The proxy then forwards this request to the target site, receives the response, and relays it back to you. This process masks your real IP address, making it appear as though your internet activity originates from the proxy server's IP address instead of your own. As a result, proxy servers are a popular tool for those looking to bypass content restrictions, access geo restricted content, or simply mask your IP address for privacy.
One of the key advantages of proxy servers is their flexibility. Unlike virtual private networks, which route all your internet traffic through a secure server, proxy servers can be configured to handle only specific types of web traffic or individual applications. For example, you might use an HTTP proxy to manage browser traffic for web scraping, while your other internet connections remain direct. This targeted approach allows both proxy servers and users to optimize performance and control which data is routed through the intermediary server.
There are several types of proxy servers, each designed for different use cases. Forward proxies are commonly used within internal networks, providing a single point of access and security for groups of users. Transparent proxies operate in the background, making it seem as though you're connecting directly to the internet, while still filtering or caching content. Anonymous proxies go a step further by hiding not just your IP address, but also your device information, making your online activity much harder to trace.
Beyond privacy, proxy servers can also be used to restrict access to certain websites or online content. Organizations and parents often use proxies to enforce content restrictions, ensuring that users can only access approved sites. Additionally, many proxy servers cache frequently visited web pages, which can speed up browsing and reduce the load on the original web server.
However, it's important to understand the limitations of proxy servers. Unlike virtual private networks, proxy servers do not encrypt all your internet traffic. This means that while proxies hide your IP address and help you access geo restricted content, your sensitive data remains vulnerable to interception by unauthorized third parties. If you're handling confidential information or require a secure connection, a VPN is a better choice, as VPNs encrypt all your traffic and route it through a secure server.
In summary, proxy servers are a powerful tool for managing web traffic, accessing geo restricted content, and supporting tasks like web scraping. They offer flexibility and control at the application level, but do not provide the comprehensive data protection of virtual private networks. When deciding between a proxy server and a VPN, consider whether you need to encrypt data and protect sensitive information, or simply want to bypass content restrictions and mask your IP address for specific online activities.
Why Proxies Are Better Than VPNs
While both proxies and VPNs can hide your IP address and enhance online privacy, they serve very different needs. The key differences between a VPN and a proxy lie in their security features, encryption, and use cases: VPNs provide strong encryption and comprehensive security, while proxies mainly hide your IP address without encrypting your data.
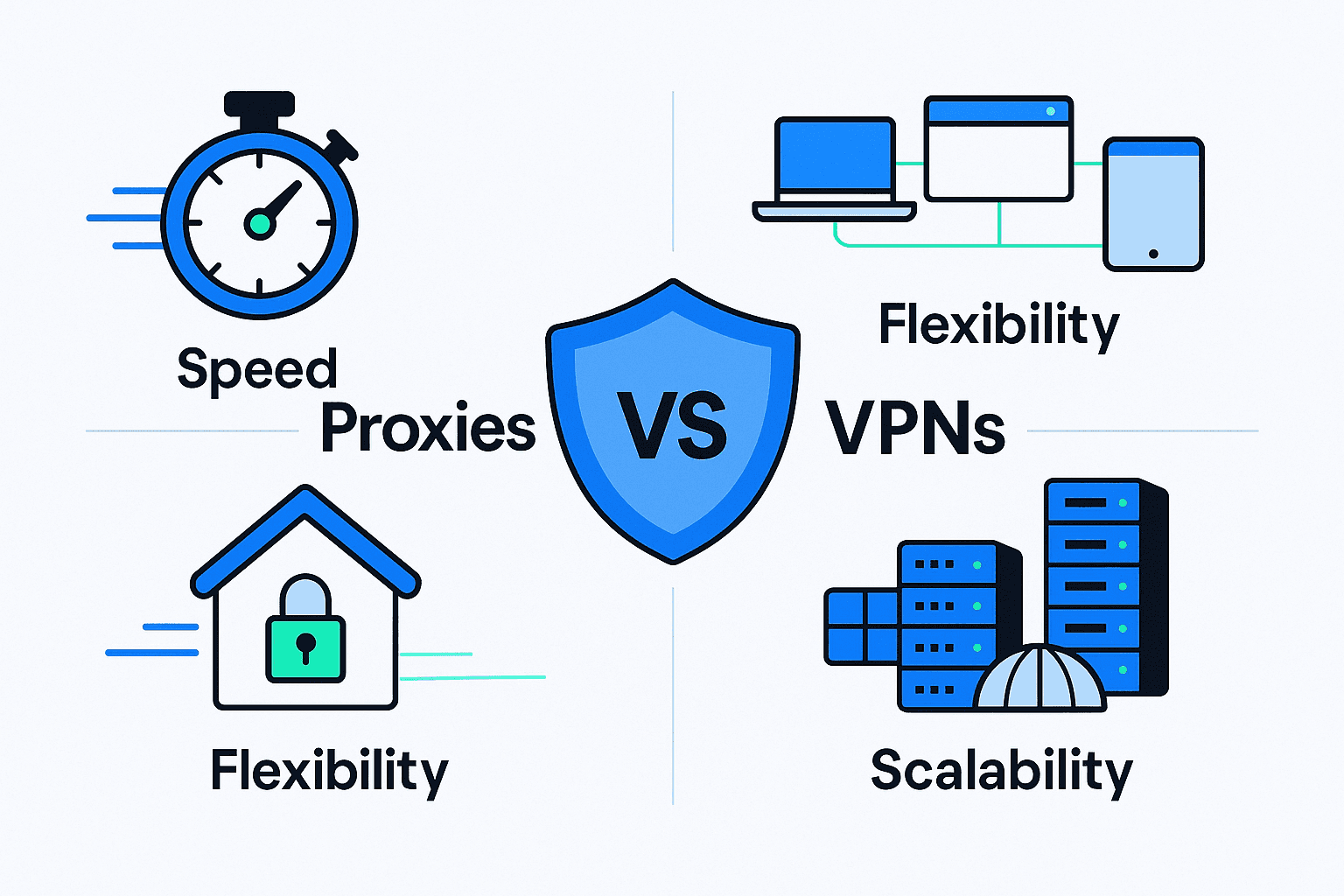
1. Speed and Performance for Internet Traffic
VPNs encrypt all your internet data, which adds latency and reduces speed. Proxies, on the other hand, do not rely on heavy encryption layers, so they maintain faster and more consistent performance.
However, free proxies and free proxy servers often have slower speeds, less reliable connections, and may not be suitable for high-performance tasks compared to paid options. Free proxy connections can be unstable, and a free proxy is generally only recommended for basic, low-risk activities. Free proxy servers and free proxies may also lack security features and can compromise privacy, making them less ideal for sensitive or demanding use cases.
This is essential for users running bots, scrapers, or multiple browser sessions where speed directly affects results.
2. Flexibility and Control
A VPN routes all traffic through a single server. A proxy allows you to assign different IPs for different tasks, sessions, or tools.
With advanced solutions like rotating residential proxies, a type of residential proxy, you can automatically switch IPs for each request, providing high flexibility and reliability for tasks such as ad verification and blocking malicious activity. Choosing reputable proxy service providers is important to ensure both performance and privacy. This level of customization is something VPNs simply can't match.
When considering proxy vs VPN, proxies generally offer greater flexibility for assigning multiple IPs and managing large-scale data activities, while VPNs focus on encrypting all traffic through a single connection.
3. Scalability
VPNs are built for individual users. Proxies are built for business-scale operations. Most proxy servers are designed to handle large numbers of concurrent connections, making them ideal for business-scale operations.
When you need to manage hundreds of concurrent connections, scrape data across regions, or monitor global search results, proxies offer the scalability and automation support that VPNs lack.
Whether you're an SEO professional, data analyst, or developer, proxies let you scale your projects without being limited by server capacity or bandwidth restrictions. While some may consider using both a VPN and a proxy for added privacy or security, proxies alone are often sufficient for scalability in business operations.
4. Targeted Use Cases to Bypass Content Restrictions
Proxies are purpose-built for:
- Web scraping and automation
- Ad verification and SEO tracking
- Managing multiple social or e-commerce accounts
- Accessing geo-restricted data, geographically restricted content, file sharing sites, and video streaming services (for example, a UK based Netflix subscriber can use a proxy to access content from other regions)
- Using HTTP proxies for web traffic (for sensitive activities like online banking, ensure SSL enabled in your browser)
VPNs are best for:
- Browsing securely on public Wi-Fi
- Streaming geo-blocked entertainment
- Personal online privacy and private browsing
For professional or high-volume tasks, proxies are far more efficient.
5. IP Rotation, Anonymity, and Masking Your IP Address
Most VPNs assign you one IP per connection. Proxies can rotate thousands of IP addresses, especially with residential and datacenter proxy networks, which greatly enhances anonymity.
Using an anonymous proxy is especially effective for private web browsing and avoiding detection, as it conceals your identity and browser details from target websites.
This makes proxies far more effective for staying anonymous online, avoiding bans, and accessing region-specific data at scale.
The Bottom Line
While both proxies and VPNs can hide your IP address and enhance online privacy, they serve very different needs. The key differences between a VPN and a proxy lie in their security features, encryption, and use cases: VPNs provide strong encryption and comprehensive security, while proxies mainly hide your IP address without encrypting your data.
VPNs prioritize encryption and personal privacy but sacrifice speed and scalability.
Proxies prioritize speed, control, and flexibility—making them the better choice for professionals, developers, and businesses that rely on data access and automation.
Consider whether you need a VPN and a proxy together, or if just one solution is best for your specific needs.
If you're looking for a high-performance solution that delivers speed, stability, and complete anonymity, explore LightningProxies. Choosing the right VPN or proxy server depends on your specific requirements.

October 22, 2025
Comparison
Datacenter vs Residential Proxies: Key Differences, Use Cases, and IP Rotation
Understand datacenter vs residential proxies: how they work, pros/cons, IP rotation, and when to use each. Learn practical examples and best practices.

September 29, 2025
Guide
What Is a Residential Proxy: Complete Guide 2025
Learn everything about residential proxies: how they work, types, benefits, and use cases for web scraping and privacy.
October 03, 2025
Announcements
Proxy Meaning: What Does a Proxy Really Do
Discover the true meaning of proxy servers and how they work.





